This article is part of an ongoing series, “Navigating the Complexities of Setting Up a Business in the USA”. View all the articles in the series here.
Key Takeaways:
- Understand economic nexus to avoid unexpected tax liabilities when expanding your business into the United States.
- State-specific sales tax rules vary widely; compliance avoids penalties and streamlines operations.
- Consulting with tax professionals can help you navigate complex state and local taxes, enhancing your U.S. expansion strategy.
~
The U.S. continues to captivate global businesses, attracting significant foreign direct investment (FDI). It’s easy to understand why: Entering the U.S. market is a strategic move that gives your business access to a vast customer base and a thriving economy. However, this opportunity also comes with the challenge of navigating a complex tax landscape. Understanding the nuances of state and local taxes is crucial to maintaining compliance while refining your U.S. operations.
This article explores critical aspects of state and local tax issues — focusing on economic nexus, sales tax obligations, and the importance of consulting services in navigating these challenges.
Overview of State and Local Tax Complexities
The U.S. tax system is uniquely intricate, with businesses required to navigate not only federal taxes but also the varying tax rules of 50 states and many localities. As a strong influx of FDI drives more companies to establish operations in the U.S., many of these businesses find themselves unprepared for this complex tax environment. Companies must stay compliant across multiple jurisdictions — a challenge that can significantly impact your overall tax burden.
Consider a European company expanding its e-commerce operations into the U.S. The company quickly discovered that a lack of understanding of state-specific sales tax obligations led to non-compliance, resulting in costly penalties and accumulating interest. By consulting with tax professionals, the business streamlined its tax compliance processes and reduced its overall tax liability — highlighting the importance of professional guidance.
Economic Nexus
Definition and Implications of Economic Nexus
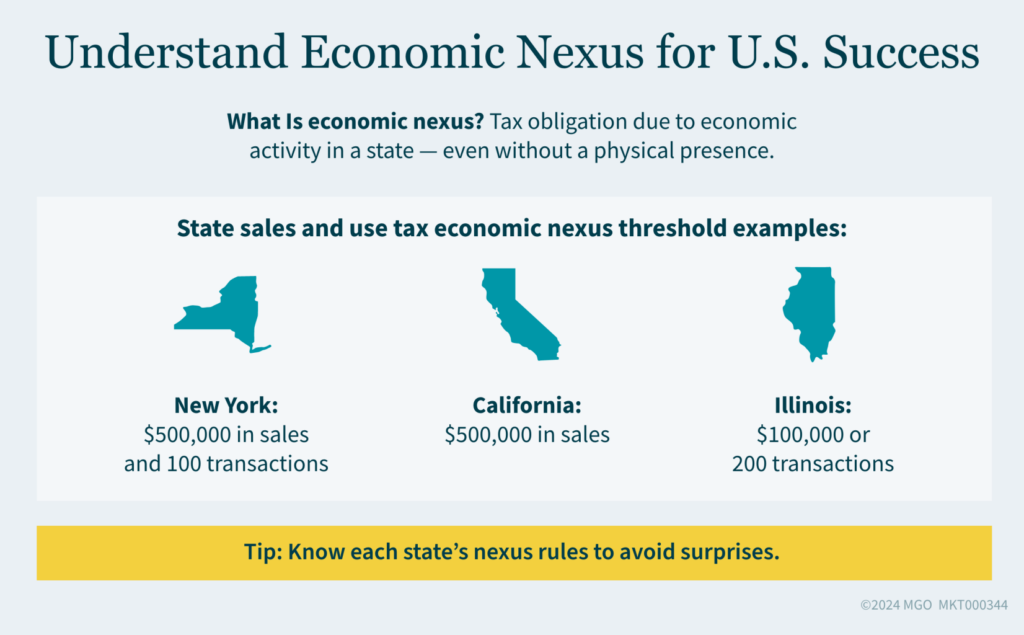
Economic nexus refers to a business’s economic activity within a state, which may create a tax obligation regardless of physical presence. This concept gained prominence following the 2018 Supreme Court decision in South Dakota v. Wayfair, Inc., which allowed states to require businesses with significant economic activity in a state to collect and remit sales tax (even if the company has no physical presence in the jurisdiction). Since the Wayfair decision, an increasing number of states are applying economic nexus for both sales and use taxes as well as state income taxes through the use of a factor presence nexus standard.
State-by-State Nexus Thresholds
It is crucial to understand each state’s threshold for economic nexus. It’s also important to understand that the economic nexus threshold for sales and use tax may not be the same as the threshold for income tax. For example, in New York, a business with more than $500,000 in sales and 100 transactions within the state must collect and remit sales tax. However, a corporation is not subject to New York corporate income/franchise tax unless its New York receipts equal or exceed $1,000,000. Other states may have higher or lower economic thresholds. Keeping track of these varying standards is essential for proper compliance.
Impact of Legislation
Changes in state and local tax laws, such as those resulting from the Wayfair decision, have far reaching implications for businesses — especially in e-commerce. Your company must continually monitor changes in state tax laws to remain compliant and avoid unexpected tax liabilities.
Sales Tax Obligations
Sales tax requirements in the U.S. are state-specific, with each state setting its own rates, rules, and exemptions. This can be particularly challenging if your company operates in multiple states, as you must manage varying tax obligations depending on the jurisdictions where you conduct business. For instance, while a good or service may be subject to sales tax in some states, it may be exempt in others.
Examples of Compliance Challenges
Compliance with state-specific sales tax rules can be complex and time-consuming. For instance, a company might face challenges in categorizing products or services as taxable or nontaxable according to each state’s tax code. Additionally, managing exemption certificates, state and local tax rates, filing deadlines, and keeping up with ever-changing tax laws can create significant administrative burdens.
Industry Specific Considerations
The sales tax challenges facing businesses vary from industry to industry. For example, an e-commerce company selling software-as-a-service (SaaS) may find its revenue is subject to sales tax in some states while not in others. To properly address the issue, the company should understand how the various states source their revenue. Then the company should review those identified states’ laws to determine how they define taxable products and services. Finally, the company needs to understand how each state applies similar laws in their own unique manner. Understanding these nuances is critical for correct tax collection and reporting.
Consulting Services
Role of Consulting in Navigating State and Local Taxes
Given the complexities of state and local tax laws, consulting with tax professionals is crucial. They can help your business understand its tax obligations, develop strategies to minimize your tax burden, and verify you are compliant with evolving state and local tax rules and regulations.
Consulting Strategies for Compliance
- Nexus studies: Consultants can conduct nexus studies to determine where a business has tax obligations, helping you avoid potential penalties for non-compliance.
- Automation tools: Consultants can assist you with implementing tax automation software to streamline the process of calculating, collecting, and remitting sales tax across multiple states.
- Audit representation: Consultants can aid with state tax audits by helping to prepare all necessary documentation, confirm the company is fully compliant with tax laws, communicate directly with the auditor, and provide nuanced arguments regarding tax positions taken.
Tax Credits and Incentives
Consultants can help businesses take advantage of state-specific tax credits and incentives, which could be a deciding factor for where to set up a new facility. For example, states like California offer significant credits for research and development (R&D) activities. Your business should conduct a comparative analysis of the tax incentives offered by different states. A state currently receiving high levels of FDI may offer significant tax credits for R&D activities or job creation, which could be critical for manufacturing companies deciding where to locate their operations. These incentives are often part of state-level strategies to attract more foreign businesses.
Emerging Trends and Future Considerations
Changes in State Tax Policy
One emerging trend is the increasing reliance on sales tax by states due to declining income tax revenues — a shift that may be partially influenced by broader economic trends, including strong FDI inflows into the U.S. Your business can prepare for these changes by staying informed about legislative updates and adjusting your tax strategies accordingly. A state and local tax consultant can play an instrumental role in assisting your company in keeping up with these trends.
Impact of Remote Work
Since COVID, the rise of remote work has further complicated state tax obligations. Companies with remote employees in multiple states may face new tax liabilities even if the business has no other physical presence (like an office). Additionally, as remote work becomes more prevalent, the tax obligations for companies with employees in multiple jurisdictions are becoming increasingly complex, further underscoring the need for proactive tax planning.
Tax Treaty Considerations
While primarily a federal issue, international tax treaties can influence state tax obligations indirectly. For instance, income tax treaties might mitigate double taxation. Although states are not parties to foreign tax treaties, your business should be aware of how state and local taxes may interact with these income treaties.
Preparing Your Business for U.S. State and Local Tax Compliance
Successfully navigating the complexities of state and local tax is a critical part of expanding your business into the U.S. By understanding economic nexus, managing sales tax obligations, utilizing consulting services, and staying ahead of emerging trends, your business can maintain compliance, avoid penalties, and improve its operations in the complex state and local tax environment. As the U.S. continues to attract significant FDI, being well-prepared and staying informed will be key to achieving long-term success.
For further insights and guidance on expanding your business into the U.S., reach out to our International Tax team today.
Setting up a business in the U.S. requires thorough planning and an understanding of various regulatory and operational challenges. In this series, we will delve into specific aspects of this process, providing guidance and practical tips. Our next article will dive into pre-arrival tax planning.